Synapsis of Homologous Pairs Occurs Crossing Over May Occur
Yes crossing over occurs during synapsis when the chromosomes are bundled in tetrads. Synapsis is the pairing of two homologous chromosomes that occur during meiosis.
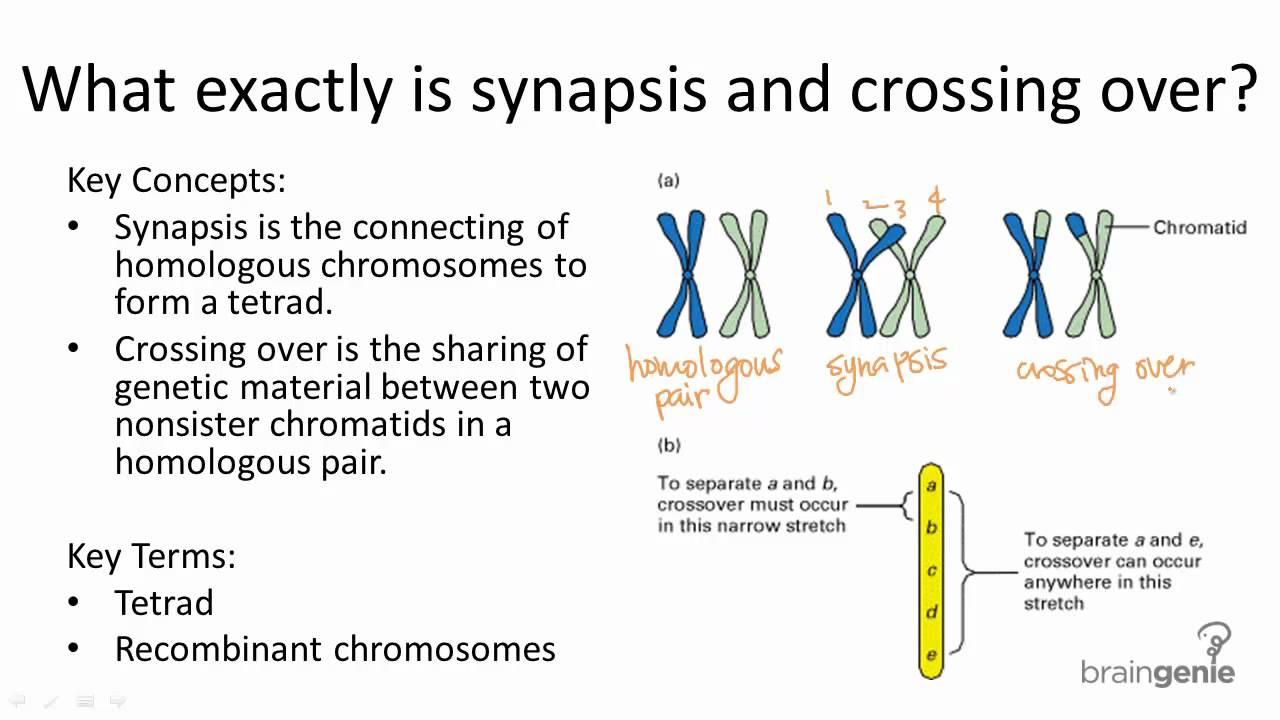
5 2 3 Synapsis And Crossing Over Youtube
This occurs in prophase of meiosis I.

. A protein complex called the synaptonemal complex connects the homologues. The main difference between synapsis and crossing over is that synapsis is the pairing of homologous chromosomes during the prophase 1 of the meiosis 1 whereas crossing over is the exchange of the genetic material during synapsis. The chromatids intertwine breaking apart and exchanging pieces with one other in a process called crossing-over.
In prophase I of meiosis the replicated homologous pair of chromosomes comes together in the process called synapsis and. Independent assortment of chromosomes. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation and possible chromosomal crossover between them.
The exchange of homologous portions of nonsister chromatids. Synapsis will ensure that each daughter cell receives one homologue from each parent and allow crossing-over. Yes crossing over occurs during synapsis when the chromosomes are bundled in tetrads.
Why does Synapsis occur in meiosis and not mitosis. Crossing over occurs in the first division of meiosis. When an area of a chromatid is exchanged with the matching area on a chromatid of its homologous chromosome its called _____ crossing over.
A 29 Centromeres of sister chromatids uncouple and chromatids separate. Synapsis mainly occurs during prophase I of meiosis I. A synapsis is the pairing of 2 homologous chromosomes.
Where does crossing over and synapsis occur. A Homologous chromosomes are separated. Meiosis I is called the reduction division because this is when the sets of homologous chromosomes get separated diploid.
C The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II. Synapsis is the pairing of two chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. A The statement is true for meiosis II only.
Crossing over process in genetics by which the two chromosomes of a homologous pair exchange equal segments with each other. Crossing over is an interchange or reciprocal exchange of segment between chromatids of a homologous pair of chromosomes resulting in a recombination of gene. Homologous chromosomes synapse and crossing over occurs.
The formation of chiasmata. Crossing over may occur. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation and possible chromosomal crossover.
At that stage each chromosome has replicated into two strands called sister chromatids. The cross-over site forms. Similarly one may ask how does crossing over occur in meiosis.
What is meant by synapsis. This occurs in prophase of meiosis I. Further genetic variation comes from crossing over which may occur during prophase I of meiosis.
D The statement is true for meiosis I only. Synapsis and crossing over. E 30 Which of the following happens at the conclusion of meiosis I.
Synapsis and crossing over occurs during the prophase 1 of meiosis 1 which is involved in the sexual reproduction of organisms. Crossing over is A. Synapsis of homologous pairs occurs crossing over may occur a I b II c IV d VI e from BIO 101 at College Preparatry School Of Ame.
Crossing over may occur. Synapsis of homologous pairs occurs. The movement of genetic material from one chromosome to a nonhomologous chromosome.
28 Synapsis of homologous pairs occurs. Synapsis is the pairing of homologous chromosomes in a cell. Does synapsis occur in Zygotene.
Synapsis or syndesis is the lengthwise pairing of homologous chromosomes. A 31 Which of the following is true of the process of meiosis. B The statement is true for mitosis only.
Synapsis is an event that occurs during meiosis in which homologous chromosomes. Hence the process of synapsis is essential for crossing-over. During synapsis crossing over may occur during which homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material.
Chromosomal crossover or crossing over is the exchange of genetic material during sexual reproduction between two homologous chromosomes non. Synapsis also called syndesis is the pairing of two homologous chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. Pachytene Crossing over of genetic material.
Zygotene Synapsis begins with a synaptonemal complex forming between homologous chromosomes. Crossing overcrossing over process in genetics by which the two chromosomes of a homologous pair exchange equal segments with each otherCrossing over occurs in the first division of meiosisAt that stage each chromosome. Making an RNA copy of a DNA strand.
The two chromosomes are held together by synaptonemal complexes which are formed by a collection of RNA with proteins. After telophase I of meiosis what is the chromosomal make up of each daughter cell. Those chromosomes pair up during meiosis prophase I where they exchange genetic material during the process of crossing-over.
During the meiosis I synapsis always occur whereas crossing-over may or may not occur. Crossing over is an interchange or reciprocal exchange of segment between chromatids of a homologous pair of chromosomes resulting in a recombination of gene. Homologous chromosomes are pair of chromosomes one inherited from father and other inherited from mother that contain the same genes but might have different alleles of those genes.
Synapsis is the pairing of two homologous chromosomes that occur during meiosis. Synapsis takes place during prophase I. Crossing-over always occurs after the synapsis.
Difference Between Synapsis And Crossing Over Definition Mechanism Function Comparison

File Synapsis And Crossing Over With Labels Png Wikimedia Commons

Synapsis Or Crossing Over Mechanism For Increasing Genetic Diversity Meiosis And Other Factors Affecting Genetic Variability Mcat Content
Comments
Post a Comment